Background
Table calculations depend upon the data in the view, not the underlying data. Tableau QuickCalculations occur as a post-database processing step.
When we select a table calc, Tableau first queries our data source (whether that be a database connection, extract, or spreadsheet). The query then returns the data for the table calc in a temporary table stored in cache. Tableau can then reference this temporary table when it needs to
We use ADVANCED mode for table calculations in 99% cases, because then when table layout is changed values are still correct
Example: In first picture compute using: Table (Down), but when we change table layout, then we will get wrong numbers, we need Table(Across) computing along
Addressing vs. Partitioning
Functions will return different values depending on how the calculation is addressed and partitioned
• Partitioning: the scope or grouping of the calculation. Defines how to group calculation. Simply instructs Tableau to repeat the calculation
Helper functions
Certain table calculation functions provide information about the relative position of an item within a partition. These can be used in a view or more commonly they are used as part of other calculations.
First( )
Returns the number of rows from the current row to the first row in the partition. For example, the view below shows quarterly sales. When FIRST() is computed within the Date partition, the offset of the first row from the second row is -1.
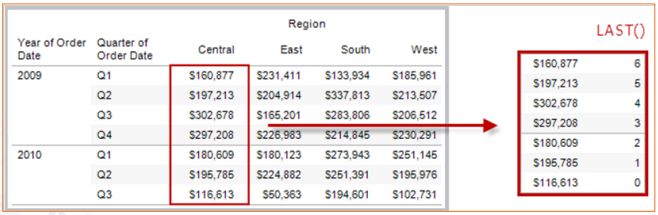
Last( )
Returns the number of rows from the current row to the last row in the partition. For example, the table below shows quarterly sales. When LAST() is computed within the Date partition, the offset of
the last row from the second row is 5
Index( )
Returns the index of the current row in the partition. The first row index starts at 1. For example, the table below shows quarterly sales. When INDEX() is computed within teh Date partition, the index of each row is 1, 2, 3, 4...etc.
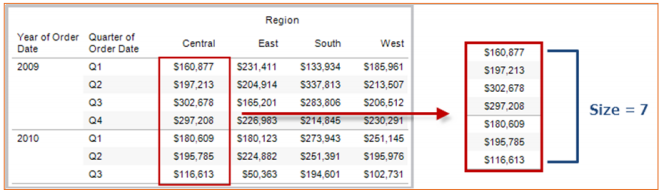
Size()
Returns the number of rows in the partition. For example, the view below shows quarterly sales. Within the Date partition, there are seven rows so the Size() of the Date partition is 7
Primary functions
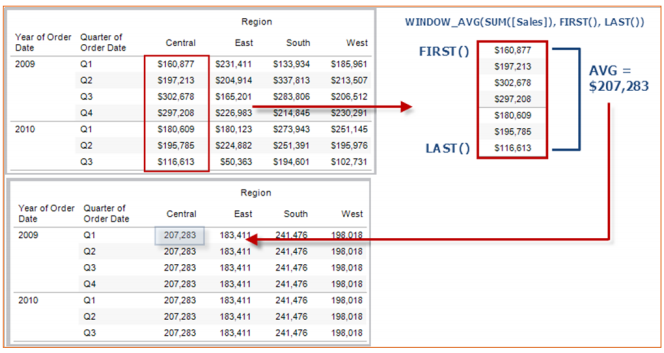
LOOKUP(expression, [offset])
Returns the value of the given expression in a target row, specified as a relative offset from the current row. Use FIRST() + n and LAST() - n for a target relative to the first/last rows in thepartition. If offset is omitted, the Compare To row may be set on the field menu. Returns NULL if the target row cannot be determined.
For example, the view below shows quarterly sales. When LOOKUP (SUM(Sales), 2) is computed within the Date partition, each row will show the sales value from 2 quarters in the future